11. WAF Web Application Firewall¶
11.1 WAF Requirements¶
Logstash installed
RSE Core
RSX Interface
11.2 File download locations¶
Download vcredist_x64.exe: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40784
Download ModSecurityIIS_2.9.3-64b.msi: https://github.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity/releases
Download filebeat: https://www.elastic.co/downloads/past-releases/filebeat-7-17-3
Download winlogbeat: https://www.elastic.co/downloads/beats/winlogbeat
Download configuration: https://github.com/tslenter/RSWAFCONF
!Notice!: filebeat version 8 > is not working with the this guide.
11.3 IIS Module installation¶
11.3.1 Visual C++ Redistributable Packages installation¶
Step 1
Start the installation of the Visual C++ Redistributable packages.

Accept and click Install.
Wait for the installation to finish.

Click close. The installation is done.
11.3.2 ModSecurity installation¶
Step 2
Start the installation of the ModSecurity package.
Click next.

Accept and click next.
Click next.

Click next.
Click Install.

Wait for the installation to finish.

Click Finish.
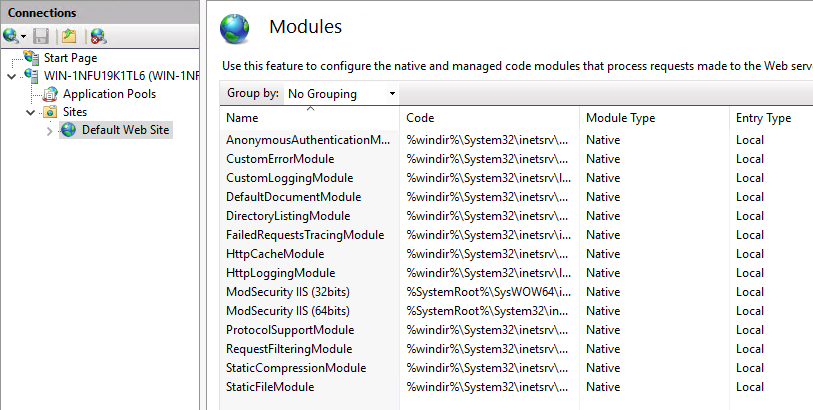
Check within the IIS console if the modules are loaded.
Depending of the installation go to section 11.3.3 (WinLogBeat) or 11.3.4 (Filebeat).
11.3.3 WinLogBeat installation¶
Step 3
Start the installation of the ModSecurity package.
Accept and click Install.

Wait for the installation to finish.
Click Finish.
11.3.4 Filebeat installation¶
Step 3
Start the installation of the ModSecurity package.
Accept and click Install.

Wait for the installation to finish.

Click Finish.
11.3.5 ModSecurity Configuration¶
Step 4
Check the RSWAFCONF git for the MODSECURITY folder and copy all files to:
C:\Program Files\ModSecurity IIS
Edit modsecurity.conf (optional):
# based on modsecurity.conf-recommended
# -- Rule engine initialization ----------------------------------------------
# Enable ModSecurity, attaching it to every transaction. Use detection
# only to start with, because that minimises the chances of post-installation
# disruption.
#
#SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly
SecRuleEngine On
# -- Request body handling ---------------------------------------------------
# Allow ModSecurity to access request bodies. If you don't, ModSecurity
# won't be able to see any POST parameters, which opens a large security
# hole for attackers to exploit.
#
SecRequestBodyAccess On
# SecStreamInBodyInspection is required by IIS for proper body inspection
# See issue #1299 for more information
SecStreamInBodyInspection On
# Enable XML request body parser.
# Initiate XML Processor in case of xml content-type
#
SecRule REQUEST_HEADERS:Content-Type "(?:application(?:/soap\+|/)|text/)xml" \
"id:'200000',phase:1,t:none,t:lowercase,pass,nolog,ctl:requestBodyProcessor=XML"
# Enable JSON request body parser.
# Initiate JSON Processor in case of JSON content-type; change accordingly
# if your application does not use 'application/json'
#
SecRule REQUEST_HEADERS:Content-Type "application/json" \
"id:'200001',phase:1,t:none,t:lowercase,pass,nolog,ctl:requestBodyProcessor=JSON"
# Maximum request body size we will accept for buffering. If you support
# file uploads then the value given on the first line has to be as large
# as the largest file you are willing to accept. The second value refers
# to the size of data, with files excluded. You want to keep that value as
# low as practical.
#
SecRequestBodyLimit 13107200
SecRequestBodyNoFilesLimit 131072
# Store up to 128 KB of request body data in memory. When the multipart
# parser reaches this limit, it will start using your hard disk for
# storage. That is slow, but unavoidable.
#
SecRequestBodyInMemoryLimit 131072
# What do do if the request body size is above our configured limit.
# Keep in mind that this setting will automatically be set to ProcessPartial
# when SecRuleEngine is set to DetectionOnly mode in order to minimize
# disruptions when initially deploying ModSecurity.
#
SecRequestBodyLimitAction Reject
# Verify that we've correctly processed the request body.
# As a rule of thumb, when failing to process a request body
# you should reject the request (when deployed in blocking mode)
# or log a high-severity alert (when deployed in detection-only mode).
#
SecRule REQBODY_ERROR "!@eq 0" \
"id:'200002', phase:2,t:none,log,deny,status:400,msg:'Failed to parse request body.',logdata:'%{reqbody_error_msg}',severity:2"
# By default be strict with what we accept in the multipart/form-data
# request body. If the rule below proves to be too strict for your
# environment consider changing it to detection-only. You are encouraged
# _not_ to remove it altogether.
#
SecRule MULTIPART_STRICT_ERROR "!@eq 0" \
"id:'200003',phase:2,t:none,log,deny,status:400, \
msg:'Multipart request body failed strict validation: \
PE %{REQBODY_PROCESSOR_ERROR}, \
BQ %{MULTIPART_BOUNDARY_QUOTED}, \
BW %{MULTIPART_BOUNDARY_WHITESPACE}, \
DB %{MULTIPART_DATA_BEFORE}, \
DA %{MULTIPART_DATA_AFTER}, \
HF %{MULTIPART_HEADER_FOLDING}, \
LF %{MULTIPART_LF_LINE}, \
SM %{MULTIPART_MISSING_SEMICOLON}, \
IQ %{MULTIPART_INVALID_QUOTING}, \
IP %{MULTIPART_INVALID_PART}, \
IH %{MULTIPART_INVALID_HEADER_FOLDING}, \
FL %{MULTIPART_FILE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED}'"
# Did we see anything that might be a boundary?
#
SecRule MULTIPART_UNMATCHED_BOUNDARY "!@eq 0" \
"id:'200004',phase:2,t:none,log,deny,msg:'Multipart parser detected a possible unmatched boundary.'"
# PCRE Tuning
# We want to avoid a potential RegEx DoS condition
#
SecPcreMatchLimit 1000
SecPcreMatchLimitRecursion 1000
# Some internal errors will set flags in TX and we will need to look for these.
# All of these are prefixed with "MSC_". The following flags currently exist:
#
# MSC_PCRE_LIMITS_EXCEEDED: PCRE match limits were exceeded.
#
SecRule TX:/^MSC_/ "!@streq 0" \
"id:'200005',phase:2,t:none,deny,msg:'ModSecurity internal error flagged: %{MATCHED_VAR_NAME}'"
# -- Response body handling --------------------------------------------------
# Allow ModSecurity to access response bodies.
# You should have this directive enabled in order to identify errors
# and data leakage issues.
#
# Do keep in mind that enabling this directive does increases both
# memory consumption and response latency.
#
SecResponseBodyAccess On
# Which response MIME types do you want to inspect? You should adjust the
# configuration below to catch documents but avoid static files
# (e.g., images and archives).
#
SecResponseBodyMimeType text/plain text/html text/xml
# Buffer response bodies of up to 512 KB in length.
SecResponseBodyLimit 524288
# What happens when we encounter a response body larger than the configured
# limit? By default, we process what we have and let the rest through.
# That's somewhat less secure, but does not break any legitimate pages.
#
SecResponseBodyLimitAction ProcessPartial
# -- Filesystem configuration ------------------------------------------------
# The location where ModSecurity stores temporary files (for example, when
# it needs to handle a file upload that is larger than the configured limit).
#
# This default setting is chosen due to all systems have /tmp available however,
# this is less than ideal. It is recommended that you specify a location that's private.
#
SecTmpDir c:\inetpub\temp\
# The location where ModSecurity will keep its persistent data. This default setting
# is chosen due to all systems have /tmp available however, it
# too should be updated to a place that other users can't access.
#
SecDataDir c:\inetpub\temp\
# -- File uploads handling configuration -------------------------------------
# The location where ModSecurity stores intercepted uploaded files. This
# location must be private to ModSecurity. You don't want other users on
# the server to access the files, do you?
#
#SecUploadDir c:\inetpub\temp\
# By default, only keep the files that were determined to be unusual
# in some way (by an external inspection script). For this to work you
# will also need at least one file inspection rule.
#
#SecUploadKeepFiles RelevantOnly
# Uploaded files are by default created with permissions that do not allow
# any other user to access them. You may need to relax that if you want to
# interface ModSecurity to an external program (e.g., an anti-virus).
#
#SecUploadFileMode 0600
# -- Debug log configuration -------------------------------------------------
# The default debug log configuration is to duplicate the error, warning
# and notice messages from the error log.
#
#SecDebugLog c:\inetpub\temp\debug.log
#SecDebugLogLevel 3
# -- Audit log configuration -------------------------------------------------
# Log the transactions that are marked by a rule, as well as those that
# trigger a server error (determined by a 5xx or 4xx, excluding 404,
# level response status codes).
#
SecAuditEngine RelevantOnly
SecAuditLogRelevantStatus "^(?:5|4(?!04))"
# Log everything we know about a transaction.
SecAuditLogParts ABIJDEFHZ
SecAuditLogFormat JSON
# Use a single file for logging. This is much easier to look at, but
# assumes that you will use the audit log only ocassionally.
#
SecAuditLogType Serial
SecAuditLog D:\MOD-Security_LOG\modsec_audit.log
# Specify the path for concurrent audit logging.
SecAuditLogStorageDir C:\MOD-Security_LOG
# -- Miscellaneous -----------------------------------------------------------
# Use the most commonly used application/x-www-form-urlencoded parameter
# separator. There's probably only one application somewhere that uses
# something else so don't expect to change this value.
#
SecArgumentSeparator &
# Settle on version 0 (zero) cookies, as that is what most applications
# use. Using an incorrect cookie version may open your installation to
# evasion attacks (against the rules that examine named cookies).
#
SecCookieFormat 0
# Specify your Unicode Code Point.
# This mapping is used by the t:urlDecodeUni transformation function
# to properly map encoded data to your language. Properly setting
# these directives helps to reduce false positives and negatives.
#
SecUnicodeMapFile unicode.mapping 20127
# Improve the quality of ModSecurity by sharing information about your
# current ModSecurity version and dependencies versions.
# The following information will be shared: ModSecurity version,
# Web Server version, APR version, PCRE version, Lua version, Libxml2
# version, Anonymous unique id for host.
SecStatusEngine On
Check the crs-setup.conf.example (Optional):
Make sure the following paranoia level is set (Optional:
SecAction \
"id:900000,\
phase:1,\
nolog,\
pass,\
t:none,\
setvar:tx.paranoia_level=2"
Greate the folowing directory:
C:\MOD-Security_LOG
Run:
cacls C:\inetpub\temp /e /p IIS_IUSRS:f
cacls C:\MOD-Security_LOG /e /p IIS_IUSRS:f
Reload the IIS service:

Click restart.
Mod security is now installed. By default we block on the OWASP ruleset. If you only want to monitor change within the modsecurity.conf the following code (Optional):
From:
#SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly
SecRuleEngine On
To:
SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly
#SecRuleEngine On
If the detection mode is changed do a reload of the service (reload from the IIS console):

To prevent a big “modsec_audit.log” create a batch file and schedule it 1 or 2 times a day. Example (Optional):
@echo off
IISReset /STOP
del "c:\MOD-Security_LOG\modsec_audit.log"
IISReset /START
Example file location (Optional):
c:\CLEAR_MOD_SEC_LOGGING.bat
If you run WinLogBeat you can disable the following configuration within the “modsecurity.conf” (Optional):
#SecAuditLog D:\MOD-Security_LOG\modsec_audit.log
#SecAuditLogStorageDir C:\MOD-Security_LOG
A batch file is not needed if the configuration of the log file is disabled using #.
11.3.6 or 11.3.7 can be followed as step 5.
11.3.6 WinLogBeat Configuration¶
Step 5
Configuration of the WinLogBeat package.
Go to the following directory:
C:\ProgramData\Elastic\Beats\winlogbeat
Edit the winlogbeat.yml:
winlogbeat.event_logs:
- name: Application
ignore_older: 72h
provider:
- ModSecurity
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["cloud.remotesyslog.com:22222"]
processors:
- add_host_metadata: ~
- add_cloud_metadata: ~
setup.template.fields: ${path.config}/fields.yml
setup.template.json.enabled: false
setup.template.overwrite: true
A Example can found here:
https://github.com/tslenter/RSWAFCONF/tree/main/WINLOGBEAT
Replace the field.yml with the file given in the following URL:
https://github.com/tslenter/RSWAFCONF/tree/main/WINLOGBEAT
Reload the WinLogBeat service:

On the server side (Logstash with the RSE Core) add the following configuration:
Create and edit a file:
nano /etc/logstash/conf.d/99-myprogram.conf
Add the following configuration:
input {
beats {
port => 22222
}
}
filter {
mutate {
rename => { "[winlog][event_data][param1]" => "message" }
}
mutate { gsub => [ "message", ".*ModSecurity: [^\[]+\[", "" ] }
mutate { gsub => [ "message", "][^\[]+$", "" ] }
kv { field_split_pattern => "] \[" value_split => " " }
# dissect { mapping => { "message" => "[%{[@metadata][timestamp]}]%{}" } }
# date { match => [ "[@metadata][timestamp]", "EEE MMM dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS yyyy" ] }
}
output {
if [host][hostname] == "SENDING_SERVER" {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"] index => "rse-myprogram"
}
}
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
Change “SENDING_SERVER” in the hostname of your host which sends logging.
11.3.7 FileBeat Configuration¶
Step 5
Configuration of the Filebeat package.
Go to the following directory:
C:\ProgramData\Elastic\Beats\filebeat
Download the FileBeat configuration with the URL below and override the files within the FileBeat configuration folder. Expect for the modules folder.
https://github.com/tslenter/RSWAFCONF/tree/main/FILEBEAT
Copy the module directory to:
C:\Program Files\Elastic\Beats\<version>\filebeat
Edit the filebeat.yml file with the server information:
output.logstash:
hosts: ["cloud.remotesyslog.com:22222"]
# Enable if CA is enabled
# ssl.enabled: true
# ssl.certificate_authorities: ["${path.config}/cacert.crt"]
Reload the Filebeat service:

On the server side (Logstash with the RSE Core) add the following configuration:
Create and edit the following file:
nano /etc/logstash/conf.d/99-myprogram.conf
Add the following configuration:
input {
beats {
port => 22222
}
}
#use with filebeat
filter {
json {
source => "message"
}
}
output {
if [host][hostname] == "SENDING_SERVER" {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"] index => "rse-myprogram"
}
}
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
Change “SENDING_SERVER” in the hostname of your host which sends logging.